Table Of Contents
Market Shortcomings And Kinesis Solution
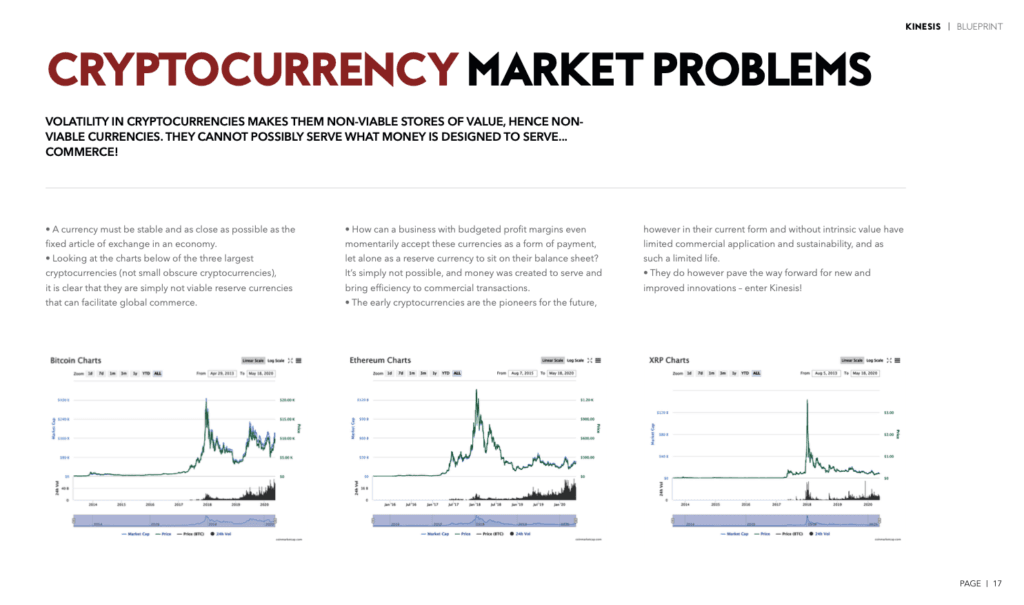
Cryptocurrency Market Shortcomings: Volatility
There are valid concerns about the suitability of cryptocurrencies as a reliable store of value and medium of exchange in commercial transactions: the fluctuating value of cryptocurrencies, which can experience significant volatility, makes them unsuitable for use as a stable currency. This uncertainty in the price of cryptocurrencies undermines their ability to serve as a reliable store of value, a fundamental function of money.
Businesses may be hesitant to accept such currencies as payment or hold them as reserves, as the lack of stability poses a significant risk to their planned profit margins. The primary purpose of money is to facilitate and streamline commercial transactions, and the current constraints of cryptocurrencies hinder their practical use in this regard.
Nonetheless, early cryptocurrencies have laid the foundation for decentralised payment systems, opening the door for advancements such as the Kinesis Monetary System.
Kinesis Solution
Kinesis currencies have the same volatility of gold and silver, which – when measured in terms of purchasing power – have shown to be much less volatile than any fiat currency.
By leveraging the time-tested properties of precious metals, kinesis currencies offer a degree of price stability that is lacking in cryptocurrencies. By virtue of being backed by physical precious metals like gold and silver, KAU and KAG have the same level of volatility as the underlying precious metals themselves. This is in contrast to traditional fiat currencies, which can experience much more significant fluctuations in their purchasing power over time. The stability of gold and silver prices, when measured in terms of their ability to buy goods and services, has been well-documented. These precious metals have served as reliable stores of value for centuries, maintaining their purchasing power even as fiat currencies issued by governments have often lost value due to inflation, economic instability, and other factors.
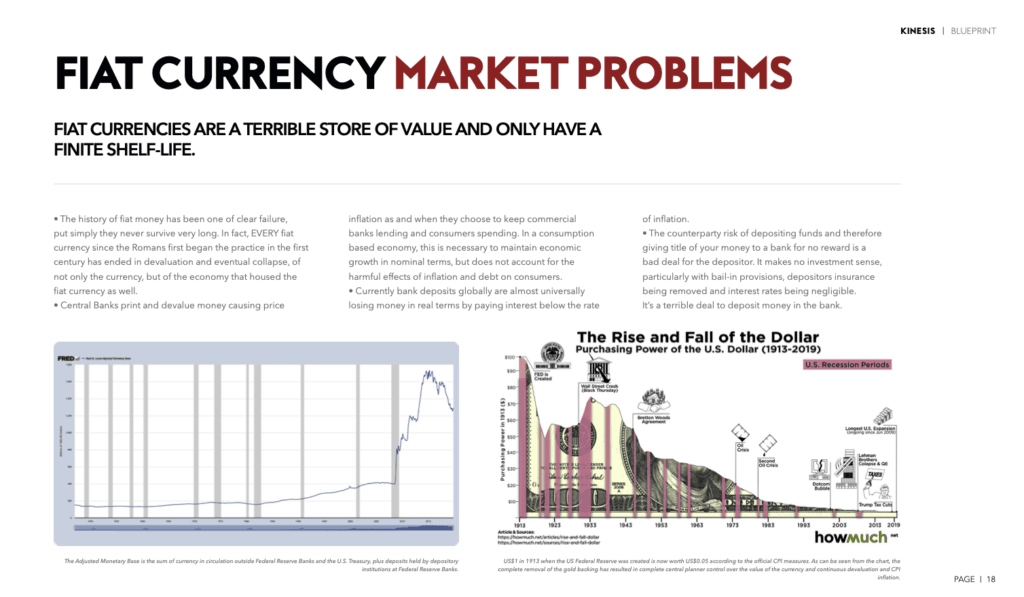
Fiat Currency Market Shortcomings
Governments and central banks worldwide have increasingly relied on aggressive monetary policies, including the printing and devaluation of national currencies, as a strategy to stimulate economic growth. While initially effective, these measures are showing diminishing returns and causing a range of adverse effects.
1. The Mechanism and Intent of Currency Devaluation
- Market Flooding: By increasing the money supply, governments aim to:
- Boost Lending: Encourage commercial banks to extend more credit.
- Stimulate Consumer Spending: Drive higher nominal economic activity through increased consumption.
- Diminishing Benefits: Over time, these policies lose their potency, as their long-term effects outweigh the short-term economic gains.
2. Impact on Purchasing Power and Savings
- Price Inflation: Deliberate currency devaluation leads to higher prices for goods and services, eroding the real value of money.
- Savings Depletion: Deposits often yield interest rates that are lower than the rate of inflation, resulting in a real-term loss for savers. As a result, individuals see their savings and incomes decline in value as inflation outpaces nominal interest rates.
3. Risks Associated with Bank Deposits
- Financial Fragility of Banks: Depositors face risks from banks that may lack financial sustainability, including:
- Bail-In Provisions: In times of crisis, deposits could be used to recapitalize struggling banks.
- Removal of Insurance: Reduced or eliminated deposit insurance leaves savers vulnerable.
4. A Global Trend with Widespread Consequences
- Deficit Funding: Governments worldwide increasingly rely on central bank funding to cover spending and debt obligations.
- Historical Precedents: Excessive money creation has historically led to currency crashes, high inflation, and even hyperinflation in extreme cases, undermining financial stability and jeopardising the economic well-being of individuals and communities.
In Summary
The pervasive reliance on money printing and currency devaluation poses serious concerns:
- Erosion of Wealth: Persistent inflation reduces the value of personal, corporate and national wealth.
- Economic Inequality: Lower-income households are disproportionately affected, as they spend a greater share of their income on necessities.
- Instability in Financial Systems: Excessive monetary interventions risk destabilizing global markets and economies.
Kinesis Solution
Gold & silver can’t be printed.
Asset Backed Currencies Shortcomings
1. Gresham’s Law: “Bad Money Drives Out Good Money”
Gresham’s Law illustrates that people tend to hoard valuable assets (like gold and silver) while spending less valuable ones (e.g., fiat currency). This phenomenon leads to the underutilization of precious metals in transactions, undermining their practical role as a medium of exchange.
- The Kinesis Solution:
- Incentivized Circulation:
- Kinesis encourages the use of its gold- and silver-backed currencies, KAU and KAG, through tangible rewards for transactions and holding.
- Velocity-Based Rewards:
- Users receive bonuses tied to the velocity of money (how often it circulates).
- Behavioral Shift:
- By rewarding activity, the system counters hoarding tendencies, fostering widespread adoption and practical use of sound money.
- Incentivized Circulation:
2. Yield: The Challenge of Income Generation
Precious metals do not naturally generate income and often incur holding costs, making them less attractive compared to:
- Interest-bearing accounts.
- Dividend-paying stocks.
3. Security: Trust and Transparency in Asset-Backed Currencies
Fraud and mismanagement of precious metal reserves have eroded trust in asset-backed currencies. Concerns about transparency and the authenticity of underlying assets make users hesitant to adopt such systems.
Kinesis Solution
The Kinesis Monetary System addresses three critical challenges of traditional cryptocurrencies and asset-backed currencies:
- Gresham’s Law is countered through incentives for deploying good money.
- Yield Limitations are overcome by introducing rewarding mechanisms for holding and transacting.
- Security Concerns are mitigated with blockchain-based transparency and robust verification.
Bullion Market Shortcomings
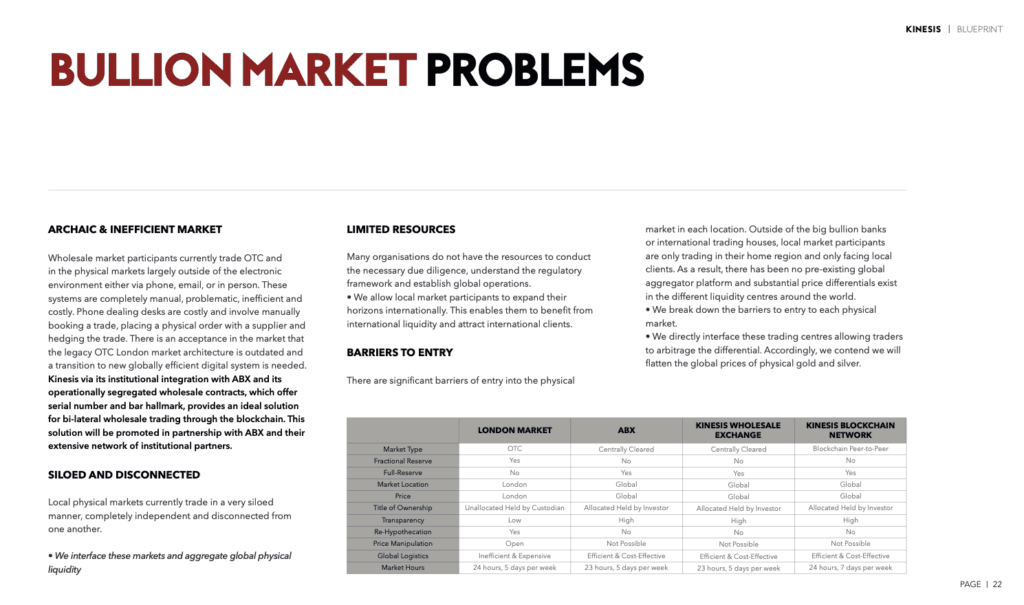
1. Antiquated and Inefficient Market
- Problem:
The current bullion market relies heavily on Over-The-Counter (OTC) transactions conducted manually via phone, email, or in-person interactions. This outdated approach requires manual trade bookings, order placements, and hedging, leading to inefficiencies, high costs, and operational bottlenecks. - Kinesis Solution:
Kinesis, through its partnership with ABX, offers a blockchain-based trading platform for bilateral wholesale trading. This system replaces the antiquated OTC structure with a digital, automated trading environment, streamlining processes and reducing costs.
2. Market Isolation and Inefficiency
- Problem:
Local physical bullion markets operate in isolation, disconnected from one another. This siloed structure prevents the formation of a globally efficient liquidity platform. - Kinesis Solution:
Kinesis aims to create a global physical liquidity network, integrating disparate markets into a unified ecosystem. This connection fosters greater efficiency and global price standardization.
3. Limited Resources for Market Participation
- Problem:
Many regional market participants lack the knowledge, resources, or infrastructure to navigate international regulations, conduct due diligence, or expand their operations globally. - Kinesis Solution:
The Kinesis system enables smaller players to access a global audience. By offering a compliant and easy-to-navigate platform, it empowers local participants to benefit from global liquidity and reach international customers.
4. Barriers to Entry
- Problem:
High barriers to entry in the global physical bullion market restrict local participants to regional trading, leading to pricing disparities between markets. - Kinesis Solution:
By integrating trading centres, Kinesis eliminates these barriers, enabling participants to arbitrage price differences and access a wider customer base, ultimately enhancing market efficiency.
5. Lack of Access for Producers and Manufacturers
- Problem:
Precious metals producers, manufacturers, and end-users (e.g., jewellers) face significant challenges entering the wholesale market as this often involve multiple intermediaries, inflating costs and complicating processes. - Kinesis Solution:
Kinesis provides a direct entry point into the wholesale market for producers, manufacturers, and end-users. By bypassing intermediaries, it reduces transaction costs and simplifies access for participants such as jewellers and investors.
Kinesis Solution
In the traditional precious metals market, producers are often forced to sell their metal through a middleman, such as a broker or dealer. This middleman takes a cut of the profits, drastically reducing the earnings for the producers.
In contrast, the ABX exchange offers a different approach that aims to empower suppliers and end-users alike. ABX enables suppliers to act as liquidity providers, giving them the ability to directly access the exchange and sell their metal at the “Offer” price, rather than the lower “Bid” price set by middlemen. This direct market access allows suppliers to capture a larger portion of the profits from their sales. Furthermore, by integrating the physical transaction cycle into the exchange, ABX makes it possible for end-users, such as manufacturers or investors, to also access the exchange directly, bypassing the traditional multi-layered distribution channels.
The founders of ABX and Kinesis believe that this shift in the dynamics of price makers and takers in the physical precious metals market could have a significant impact on price discovery. Currently, the price of precious metals is largely determined by trading activity in the futures and over-the-counter markets, which are often decoupled from the physical supply and demand fundamentals. By enabling direct participation of both suppliers and end-users on the ABX exchange, the founders hope to bring the price discovery process closer to the realities of the physical market.
Moreover, the ABX team expects that by empowering producers to sell directly on their platform, they can attract the wider industry to join the exchange. This could create a virtuous cycle, where more suppliers and end-users engage with the ABX platform, further enhancing the transparency and liquidity of the precious metals market. The ultimate goal is to establish ABX as a central hub for physical precious metals trading, challenging the dominance of traditional intermediaries and bringing more efficiency and fairness to the industry.